3D body calculators are revolutionizing how we interact with our physical forms, offering a powerful blend of technology and personalized data. These digital tools use sophisticated algorithms and various input methods to create three-dimensional models of the human body, providing detailed measurements and visualizations. This allows for a range of applications, from tailoring clothing to improving healthcare practices.
From simple measurements to advanced image processing, these tools offer unprecedented accuracy in body representation. Understanding the underlying technology, the various applications, and the ethical considerations surrounding data privacy is crucial for leveraging the full potential of this rapidly evolving field.
Understanding 3D Body Calculators
3D body calculators are software applications that generate three-dimensional models of the human body based on inputted measurements. These tools utilize various algorithms and technologies to create accurate representations, offering diverse applications across multiple industries. This section delves into the types, underlying mechanisms, accuracy, and presentation of results from different 3D body calculators.
Types of 3D Body Calculators
Several types of 3D body calculators exist, each employing different input methods and algorithms. Some rely on manual entry of anthropometric data (height, weight, various circumferences), while others utilize image processing techniques to extract measurements from photographs or 3D scans. Advanced versions may incorporate machine learning to refine model accuracy and personalize results.
Algorithms and Technologies
The core of a 3D body calculator lies in its algorithms. Common approaches include geometric modeling, where the body is represented as a collection of interconnected shapes, and surface modeling, which creates a smooth, realistic surface. These algorithms often leverage techniques like spline interpolation and surface fitting to create accurate representations. Technologies like photogrammetry, which reconstructs 3D models from multiple photographs, and structured light scanning, which projects patterns of light onto the body to capture its shape, are also commonly employed.
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison
The accuracy of 3D body calculators varies significantly depending on several factors, including the input method, the algorithm used, and the quality of the input data. Calculators relying on manual input are prone to errors due to potential inaccuracies in measurement. Image-based methods, while potentially more convenient, are susceptible to errors from lighting conditions, clothing, and posture. Generally, calculators utilizing high-quality 3D scans offer the highest level of accuracy.
A comparative study evaluating various commercial and research-grade 3D body scanners would provide quantitative data on accuracy levels.
Result Presentation
3D body calculators present their results in various formats. Some display a 3D model that can be rotated and viewed from different angles. Others provide numerical data, such as body segment lengths and circumferences. Many offer both visual and numerical outputs, allowing users to analyze the results in detail. Some advanced tools allow for customization of the model, such as changing the body’s proportions or adding clothing.
Applications of 3D Body Calculators
The applications of 3D body calculators extend across diverse fields, impacting the way products are designed, healthcare is delivered, and even entertainment is created. This section explores key applications and provides a comparative overview.
Applications in Fashion and Healthcare
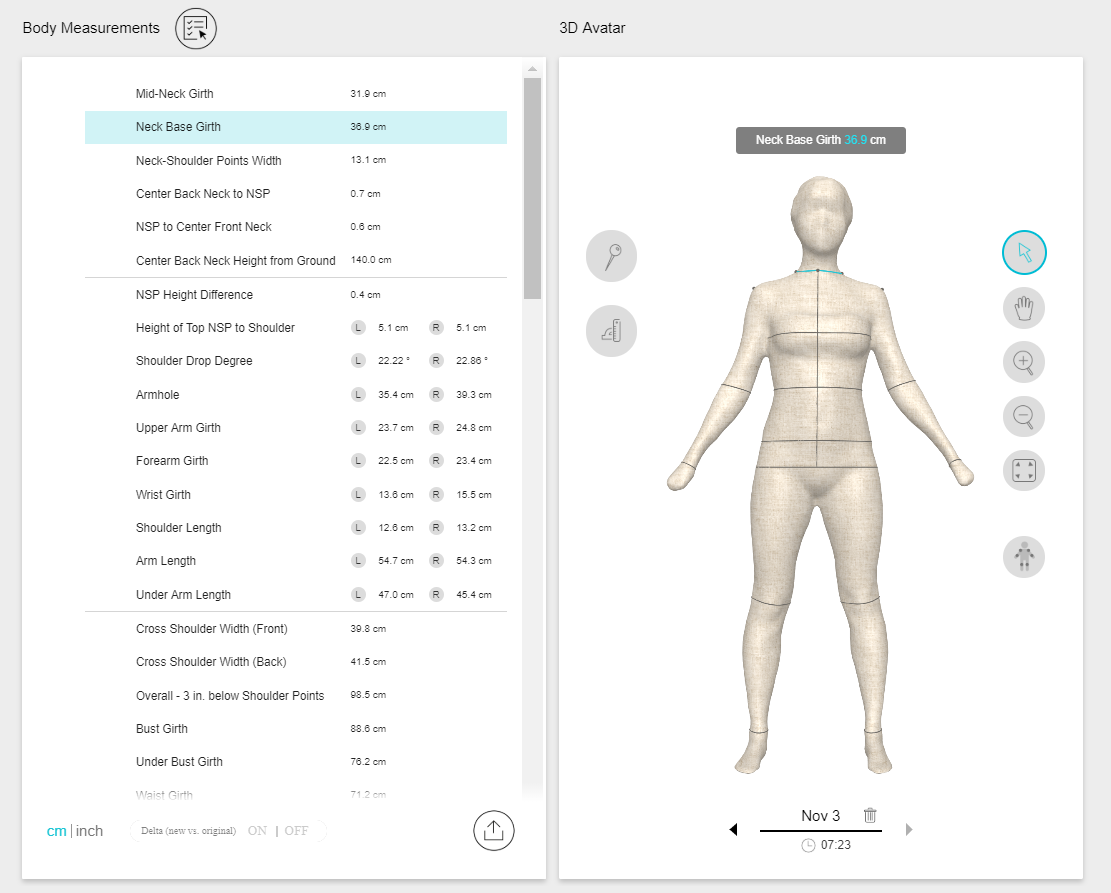
Source: bodi.me
In the fashion industry, 3D body calculators are revolutionizing clothing design and sizing. They allow designers to create virtual prototypes and tailor clothing to individual body shapes, reducing the need for physical prototypes and improving fit. In healthcare, these calculators are used to create personalized prosthetics, orthotics, and medical implants. They also aid in the development of personalized medicine, enabling doctors to better understand patient anatomy and tailor treatments accordingly.
3D body calculators offer a fascinating glimpse into personalized health metrics, allowing users to visualize their body composition. However, understanding the impact of lifestyle choices on one’s well-being requires broader context; for instance, checking local news, such as the norwalk ct arrest log , can highlight the consequences of poor decisions. Ultimately, using a 3D body calculator alongside informed lifestyle choices contributes to a healthier, more balanced life.
Other Applications
Beyond fashion and healthcare, 3D body calculators find applications in ergonomics (designing workspaces and equipment to fit the human body), animation (creating realistic characters), and gaming (developing personalized avatars). The ability to create accurate and detailed 3D models of the human body has broad implications across these and other fields.
Comparative Table of Applications
| Industry | Application | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fashion | Virtual prototyping, personalized sizing | Reduced costs, improved fit | Data privacy, accuracy of measurements |
| Healthcare | Prosthetics, orthotics, personalized medicine | Improved patient outcomes, tailored treatments | Cost, data security, regulatory compliance |
| Ergonomics | Workspace design, equipment fitting | Increased comfort, reduced injuries | Data acquisition, model validation |
| Animation/Gaming | Character creation, avatar personalization | Enhanced realism, immersive experiences | Computational resources, model complexity |
Data Input and Processing
The accuracy and effectiveness of a 3D body calculator depend heavily on the input methods and the subsequent processing of that data. This section details the input processes, model generation, and the crucial role of anthropometric data.
Data Input Methods
Several methods exist for inputting body measurements. Manual input involves entering measurements directly into the calculator, often requiring a large number of measurements. Image upload allows users to upload photos or 3D scans of their body, which the calculator then processes to extract measurements. The choice of method affects both the convenience and the accuracy of the resulting 3D model.
3D Model Generation
Once the data is input, the calculator uses algorithms to generate a 3D model. This process typically involves creating a skeletal structure representing the body’s proportions, followed by adding surface details based on the input measurements. Advanced techniques, such as surface reconstruction from point clouds, may be used to create more realistic models.
Role of Body Proportions and Anthropometric Data
Accurate anthropometric data, including measurements of body segments and proportions, is crucial for generating a realistic 3D model. The calculator uses these data to determine the relative sizes and shapes of different body parts, ensuring the model accurately reflects the individual’s physique. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to significant errors in the generated model.
Steps in Using a 3D Body Calculator
- Select a 3D body calculator.
- Choose a data input method (manual input, image upload, etc.).
- Input the necessary measurements or upload images/scans.
- Allow the calculator to process the data and generate a 3D model.
- Review the generated model and adjust parameters as needed.
- Download or export the model in the desired format.
Accuracy and Limitations
While 3D body calculators offer valuable tools, understanding their limitations and potential sources of error is essential for responsible use. This section discusses factors influencing accuracy and identifies inherent limitations.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
Several factors can affect the accuracy of 3D body calculations. These include the quality of the input data (inaccurate measurements, poor image quality), the algorithm used for model generation, and the limitations of the underlying model (simplifications in body representation). For instance, variations in posture during image capture can significantly influence the accuracy of measurements extracted from images.
Limitations and Implications
A key limitation is the inherent simplification of the human body in the models. 3D models are often based on average body proportions, and may not accurately capture the unique features of individual bodies. This can lead to inaccuracies in clothing fit and medical device design. Another limitation stems from the difficulty in accurately capturing soft tissue variations, which can affect the precision of the model.
Comparison of Calculation Methods
Different 3D body calculation methods vary in accuracy. Methods relying on manual input are generally less accurate than those utilizing 3D scans or high-quality images. The choice of method should depend on the application and the required level of accuracy. A comparative study of different methods using a standardized dataset would be beneficial in determining the relative strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
Hypothetical Accuracy Experiment, 3d body calculator
To test the accuracy of a 3D body calculator, a controlled experiment could be designed. A group of participants would have their bodies scanned using a high-precision 3D scanner (gold standard). Their measurements would then be inputted into the 3D body calculator, and the resulting model would be compared to the 3D scan data. Key metrics, such as the differences in body segment lengths and circumferences, would be analyzed to assess the accuracy of the calculator.
Ethical Considerations and Privacy: 3d Body Calculator
The use of 3D body calculators raises important ethical and privacy concerns, particularly regarding the collection and use of personal data. This section explores these issues and proposes guidelines for responsible use.
Ethical Concerns
Potential ethical concerns include the potential for misuse of body data, the risk of biased algorithms perpetuating stereotypes, and the lack of transparency in data processing. For example, if a 3D body calculator is used to assess attractiveness, it could lead to body image issues. Ensuring that data is used responsibly and ethically is paramount.
Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are crucial when handling personal body data. Robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, must be implemented to protect data from unauthorized access and misuse. Compliance with relevant data protection regulations is essential.
Recommendations for Responsible Use
Responsible use of 3D body calculators requires transparency in data collection and usage, informed consent from users, and robust data security measures. Clear guidelines on data storage and retention should be established, and users should be given control over their data.
Hypothetical Privacy Policy
A hypothetical privacy policy for a 3D body calculator application would include statements on data collection practices, data security measures, user rights (access, correction, deletion), data retention policies, and procedures for handling data breaches. It would also clarify how user data is used and shared, ensuring transparency and user control.
Future Developments
The field of 3D body calculators is constantly evolving, with ongoing advancements in technology and expanding applications. This section explores potential future developments and innovative applications.
Potential Future Improvements
Future developments may include improved algorithms for more accurate and realistic model generation, integration with wearable sensors for real-time body data capture, and the use of AI to personalize model creation and analysis. Improved data privacy and security measures are also crucial for future development.
Integration with Other Technologies
Integration with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies will create immersive experiences for users. Imagine trying on clothes virtually using a 3D model generated from a quick phone scan, or experiencing personalized medical simulations using a highly accurate 3D body representation. This integration could revolutionize the way people interact with technology and their own bodies.
Innovative Future Applications
Future applications could extend to personalized healthcare planning, where 3D body models are used to simulate surgical procedures or predict the effectiveness of different treatments. In the fashion industry, it could enable the creation of highly customized garments on demand. In the field of sports, it could be used to optimize athletic performance by creating personalized training plans.
Visual Representation of a Future Application
Imagine a virtual fitting room integrated into an online clothing store. A user takes a few photos of themselves using their smartphone. The application uses a sophisticated 3D body calculator to create a highly accurate 3D model within seconds. The user can then virtually try on different clothing items, seeing how they would look and fit on their unique body shape in real-time, before making a purchase.
The system provides detailed measurements and suggests optimal sizes, significantly reducing the need for returns and improving customer satisfaction. This is enhanced by AR overlays, showing the clothes directly on the user’s reflection in their own mirror, creating a seamless and engaging shopping experience.
Last Word
3D body calculators represent a significant advancement in personalized measurement and modeling. Their applications span numerous industries, offering solutions for customized products and improved healthcare outcomes. While challenges remain regarding accuracy and data privacy, ongoing developments promise even more precise and versatile tools in the future, ultimately enhancing our understanding and interaction with the human form.
